Define Resting Membrane Potential and Describe Its Electrochemical Basis
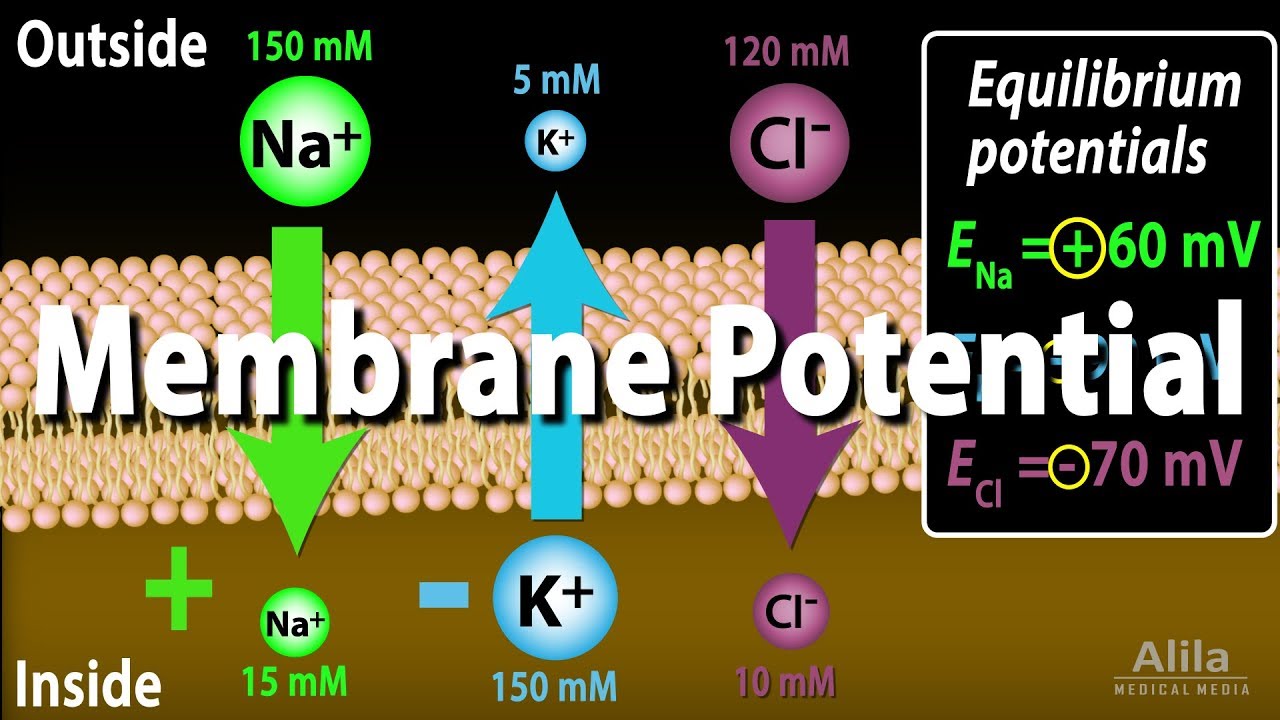
Typically the value for resting membrane potential in a neuron is -70mV meaning the neuron is polarized and the intracellular fluid has a higher concentration of negative ions and is more electrically. This resting potential is created by a concentration gradient of sodium ions and potassium ions.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11526/Sodium-Potassium-Pump.png)
Membrane Potential Definition Equilibrium Ions Kenhub
Provide specific examples of how the 4 essential concepts relative to resting membrane potential.
. A resting membrane potential opposes the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena in neurons. Define resting membrane potential state its typical value for neurons and describe its electrochemical basis ie. Compare and contrast graded and action potentials.
The resting membrane potential is a result of different concentrations inside and outside the cell. Define resting membrane potential and describe its electrochemical. Define resting membrane potential and describe its electrochemical basis.
Provide specific examples of how the 4 essential concepts relative to resting membrane potential or disruption of resting membrane potential. Describe how it is established and maintained in neurons RMP - Degree of the difference of eletrical charge between points. Define resting membrane potential and describe its electrochemical basis.
Resting membrane potential can be defined as the amount of difference in electrical charge between the ionic makeup of the extracellular fluid and intracellular fluid of a cell. A resting non-signaling neuron has a voltage across its membrane called the resting membrane potential or simply the resting potential. 1 Define resting membrane potential 2 state its typical value for neurons and 3 describe its electrochemical basis ie describe how it is established and maintained in neurons.
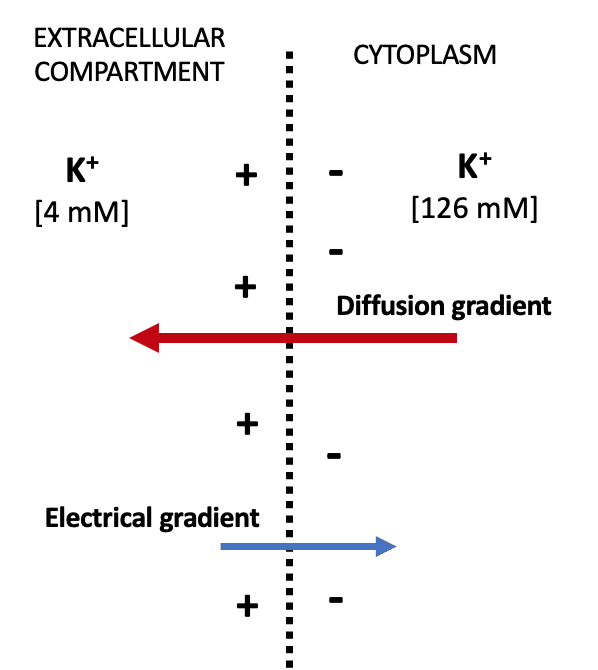
When the chemical and electrical gradients are equal in size the ion is said to be in electrochemical equilibrium and the membrane potential established is the equilibrium potential Veq for the ion. Define resting membrane potential and describe its electrochemical basis. The membrane potential of a neuron is described as the voltage difference between the intercellular and extracellular space in a non-activenon-stimulated neuron.
Sodium-potassium ion pumps in the membrane pump sodium out of and potassium into the cell. Solution for Define resting membrane potential and describe its electrochemical basis. Define resting membrane potential and describe its electrochemical basis.
Dara Byler EXSC 224 Dr. Typical value for neuron is -70mV. Briefly discuss changes to resting membrane potential.
Define resting membrane potential state its typical value for neurons and describe its electrochemical basis ie describe how it is established and maintained in neurons RMP - Degree of the difference of eletrical charge between points. Thompson 16 May 2016 Assignment 1 1. Traditionally the electrical potential difference across a cell membrane is expressed by its value inside the cell relative to the extracellular environment.
Define resting membrane potential and describe its electrochemical basis. Start your trial now. Briefly discuss changes to resting membrane potential.
12 The resting membrane potential is the result of. First week only 499. Define resting membrane potential and describe its electrochemical basis.
If the inside of a cell becomes electronegative ie if the potential difference or the voltage reaches a level higher than that of the resting potential then the membrane or the cell becomes hyperpolarized. Describe how the resting membrane potential is generated. Provide specific examples of how the 4 essential concepts relative to resting membrane potential or disruption of resting membrane potential.
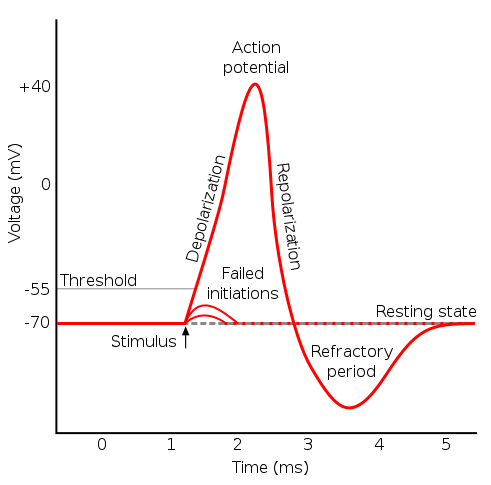
The resting potential is determined by concentration gradients of ions across the membrane and. That is to say that there is an electrical potential difference between the inside of the cell and the surrounding bathing medium of the cell. In a later lecture on the neuronal action potential we will see that the action potential ie electrical impulse is responsible for much of communication in the nervous system and that it involves a rapid reversal of the membrane potential such that the potential inside of the cell transiently becomes positive with respect to the outside before it returns back.
Resting Membrane Potential. C In the system described above opening of K channels leads to the establishment of a membrane potential which grows in size until it. Define resting membrane potential and describe its electrochemical basis.
Generation of an action potential involves a transient increase in Na permeability followed by restoration of Na impermeability and then a short-lived increase in K permeability. This fact implies that the resting membrane is more permeable to K than to the other ions listed in Table 21 and that this permeability is the source of resting potentials. By signing up youll get thousands of step-by-step solutions.
In most neurons the resting membrane potential equals. How does resistance training manage diabetes and decrease cardiovascular risksDefine resting membrane potential and describe its electrochemical basis. The difference in the number of positively charged potassium ions K inside and outside the cell dominates the resting membrane potential Figure 2.
Briefly discuss changes to resting membrane potential. Since the resting membrane potential of the squid neuron is approximately -65 mV K is the ion that is closest to being in electrochemical equilibrium when the cell is at rest. Define resting membrane potential and describe its electrochemical basis.
Explain how action potentials are generated and propagated along neurons. RMP - Degree of the difference of eletrical charge between points. Define resting membrane potential and describe its.
The resting membrane potential of a cell is defined as the electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane when the cell is in a non-excited state. The resting membrane potential on a neuron membrane will be. It is known as the action potential and graded membrane potential.
Cells of multicellular organisms such as animals and plants as well as those of unicellular organisms such as yeast exhibit a potential difference across the cell plasma membrane.

Membrane Potential Foundations Of Neuroscience
Action Potential The Resting Membrane Potential Generation Of Action Potentials Teachmephysiology
Resting Membrane Potential Nernst Generation Teachmephysiology

Membrane Potential Equilibrium Potential And Resting Potential Animation Youtube
No comments for "Define Resting Membrane Potential and Describe Its Electrochemical Basis"
Post a Comment